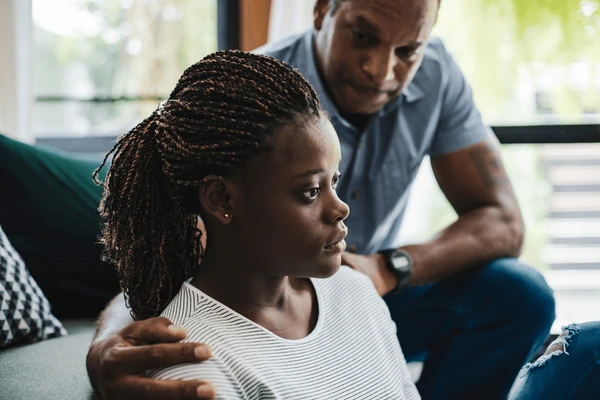
How to Support Their Journey with Chronic Illness and Mental Health
Empower teens facing chronic illness and mental health challenges. Discover strategies and resources to support their journey.
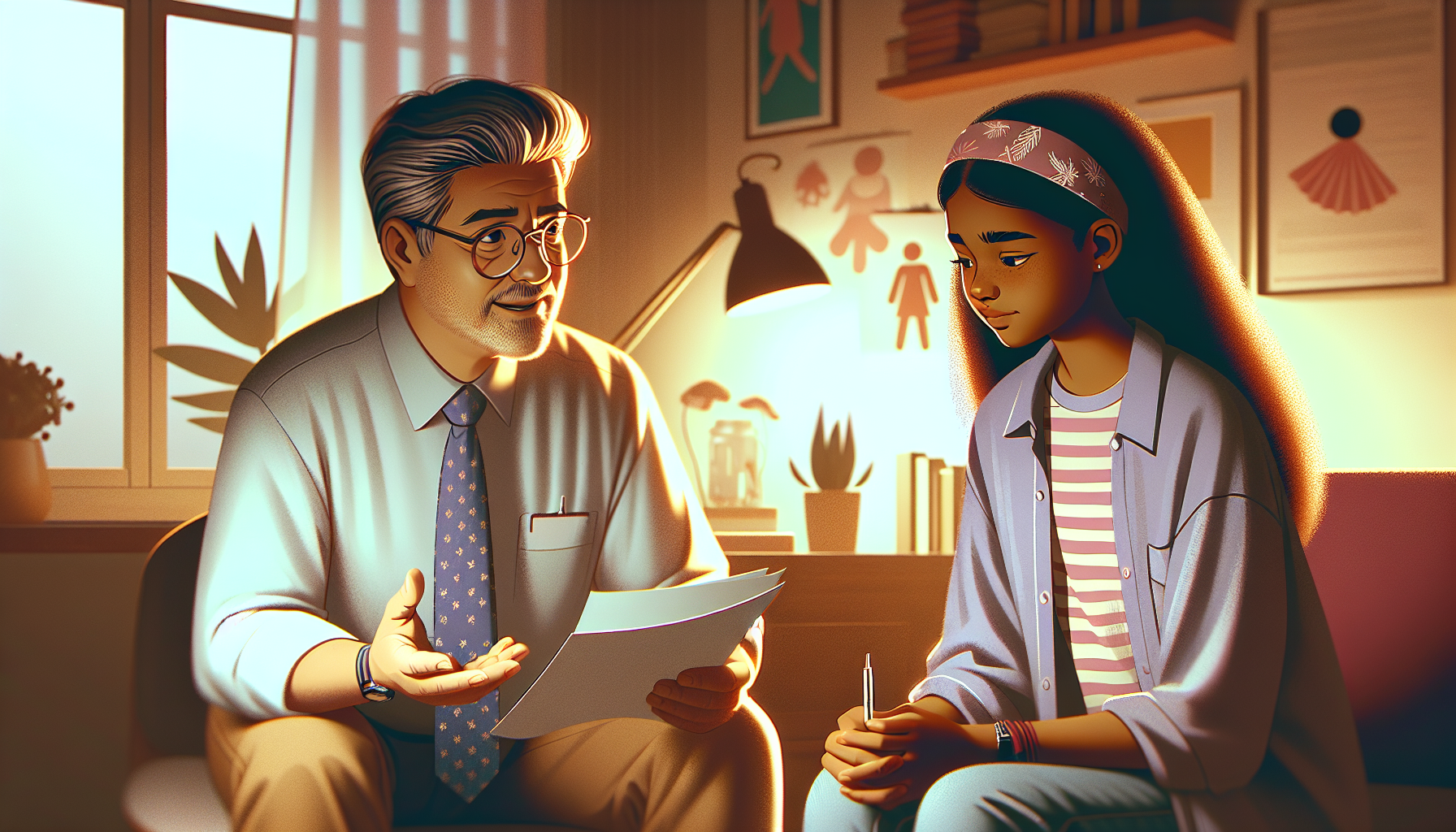

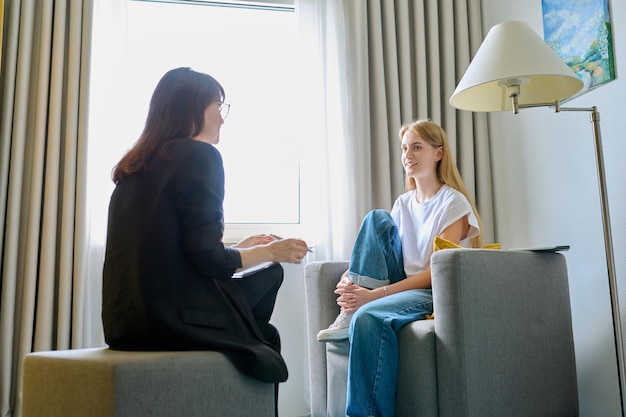
Supporting Teens with Chronic Illness
When it comes to supporting teenagers with chronic illness, it is crucial to understand the nature of chronic conditions and their impact on adolescents' development. Chronic illnesses are defined as conditions that last longer than six months, with some substantially limiting daily life or requiring extended periods of care and supervision [1]. It is estimated that 20-30% of teenagers have a chronic illness, and 10-13% have a chronic condition that significantly affects their daily life [1].

Understanding Chronic Conditions
Chronic conditions in adolescence can affect various aspects of development, including physical, cognitive, social, and emotional spheres. The prevalence of chronic illnesses in adolescence, such as diabetes (types 1 and 2), asthma, and even cancer, has increased, and more children with congenital or chronic conditions are surviving into adolescence. This shift has brought about new challenges as conditions that were once seen only in young children are now seen beyond childhood and adolescence.
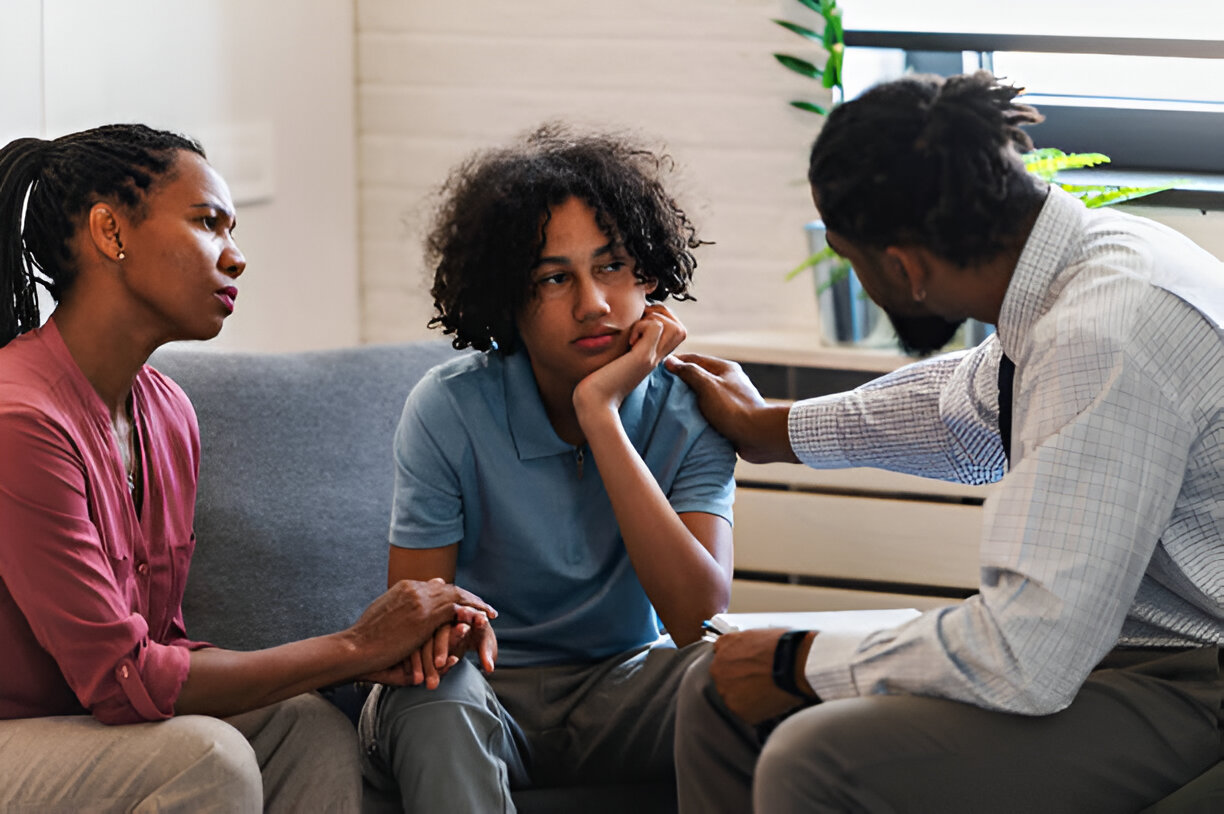
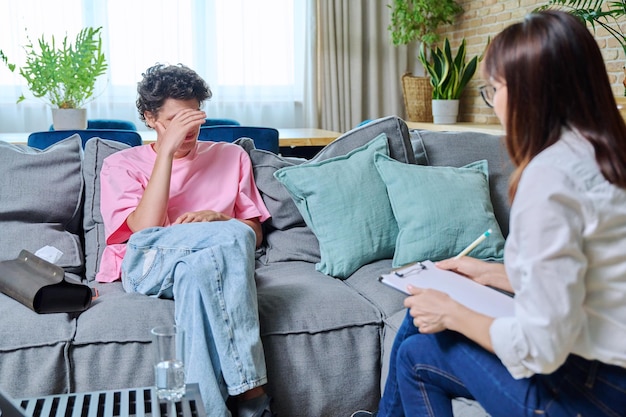
The impact of chronic illness on adolescents goes beyond their physical health. Teenagers often face concerns about their physical appearance, independence, and relationships with peers, which can complicate their development during this crucial stage. Fears or distortions related to their bodies, interference with independence from parents, and disruptions in social interactions can intensify these concerns.
Impact on Adolescents' Development
The challenges posed by chronic illness can disrupt the normal developmental trajectory of adolescents. They may encounter difficulties in forming and maintaining relationships with peers, experiencing a sense of isolation or exclusion. Adolescents might also struggle with body image concerns related to their illness, which can further impact their self-esteem and overall emotional well-being.
The demands of managing a chronic illness, such as adhering to treatment plans, attending medical appointments, and monitoring symptoms, can also place additional stress on adolescents. Balancing these responsibilities with their educational commitments and personal goals can be overwhelming.
To support teenagers with chronic illness, it is crucial to involve them in discussions about their health, encourage open communication, and provide them with opportunities to express their concerns and fears. Teaching self-care skills and helping them develop coping mechanisms are essential strategies for addressing the conflicts between normal development and healthcare needs in chronically ill teens [2]. By understanding the unique challenges they face and offering support tailored to their needs, we can empower these teenagers to navigate their journey with chronic illness and promote their overall well-being.
Mental Health Challenges
When it comes to supporting teens with chronic illness, it's essential to recognize and address the mental health challenges they may face. Chronic illness can have a significant impact on the emotional well-being of adolescents, and understanding the factors affecting their mental health is crucial in providing appropriate support.
Emotional Well-being of Teens
Young people with chronic illness are more likely to have a lower level of emotional well-being compared to their healthy peers [1]. Dealing with a chronic condition can be physically and emotionally exhausting, often leading to feelings of frustration, isolation, and stress. Adolescents may experience a sense of alienation from their peers and struggle with managing their condition and navigating the healthcare system.
To support the emotional well-being of teens with chronic illness, it's important to create a nurturing and supportive environment. School policies and practices that focus on improving emotional well-being can play a significant role in meeting students' psychosocial needs and fostering healthy school environments. By implementing strategies that promote emotional resilience and provide a sense of belonging, schools can help alleviate some of the emotional challenges faced by these adolescents.
Factors Affecting Mental Health
Various factors can influence the mental health of teens with chronic illness. Global crises such as the COVID-19 pandemic, climate change, and geopolitical conflicts have significantly impacted students' mental health, leading to increased stress, anxiety, and other mental health issues [4]. These external factors can exacerbate the emotional burden already carried by adolescents with chronic illness.
Integrating mental health education into core curricula can be instrumental in equipping educators and students with vital coping skills, emotional intelligence, and overall well-being support [4]. By providing age-appropriate interventions, schools can tailor their programs to focus on building emotional literacy, self-awareness, and basic coping strategies for younger children. For adolescents, it becomes crucial to delve into stress management, understanding complex emotions, and navigating social and academic pressures.
Addressing the mental health challenges faced by teens with chronic illness requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses emotional support, education, and empowerment. By fostering resilience and providing the necessary tools to navigate their unique circumstances, we can empower these adolescents to lead fulfilling lives despite the challenges they face.
Strategies for Support
When it comes to supporting teenagers with chronic illness and mental health issues, there are various strategies that can be implemented. These strategies aim to provide resources and create a supportive environment to help adolescents navigate the challenges they face. Two key aspects of support include providing resources for teens and recognizing the role of schools in providing assistance.
Resources for Teens
Accessible resources play a vital role in supporting teenagers with chronic illness and mental health challenges. These resources provide valuable information and support for teens dealing with both physical health issues and mental well-being. They can help adolescents understand their conditions, access appropriate treatments, and find support networks. Resources may include websites, helplines, support groups, and educational materials.
By providing teens with reliable resources, they can gain knowledge and find the support they need to manage their conditions and mental health effectively. The HHS Office of Population Affairs offers a range of resources specifically tailored to adolescents with chronic conditions.
Role of Schools in Support
Schools play a crucial role in supporting teenagers with chronic illness and mental health issues. They are a vital setting for the delivery of mental health support services, as recognized by the NCBI. Schools can provide a safe environment where students feel supported and can access the necessary resources.
Schools can implement policies and practices that foster emotional well-being, creating a healthy and supportive school environment. By integrating mental health education into the core curriculum, schools can increase mental health literacy among educators and students, equipping them with coping skills and supporting overall well-being.
Furthermore, schools can provide mental health assessments and interventions, particularly during times of crises or disasters, ensuring that students receive the necessary support. Teachers and school staff can be trained to recognize signs of distress and provide appropriate referrals to mental health professionals.
Recognizing that different age groups require tailored interventions, schools can differentiate their mental health support programs. For younger children, the focus may be on building emotional literacy, self-awareness, and basic coping strategies. For adolescents, programs can delve into stress management, understanding complex emotions, and navigating social and academic pressures [4].
By acknowledging the role of schools and implementing supportive policies and programs, we can create an environment where teenagers with chronic illness and mental health issues can thrive academically, emotionally, and physically.
Supporting teenagers with chronic illness and mental health challenges requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses resources, education, and the involvement of schools. By working together, we can ensure that adolescents receive the necessary support to manage their conditions and foster their overall well-being.
Addressing Specific Needs
Adolescents with chronic illnesses require specialized support to navigate the challenges they face. One specific group that requires attention is adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes. This chronic condition not only affects their physical health but also presents unique challenges in terms of adherence to treatment.
Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM) is a chronic autoimmune disease that requires careful management of blood sugar levels. Adolescents with T1DM face additional challenges as they navigate the complexities of adolescence while managing their condition. They must balance their diabetes management with academic demands, peer relationships, and other developmental milestones. It is crucial to provide them with the necessary support and resources to help them cope with these challenges.
To effectively support adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes, it is important to prioritize education and awareness. Providing them with comprehensive information about their condition, including the importance of blood sugar control, insulin administration, and the potential long-term consequences of poor management, can empower them to take an active role in their own health.
Challenges in Adherence to Treatment
Adherence to treatment is a critical aspect of managing Type 1 Diabetes effectively. However, adolescents may face unique challenges in adhering to their prescribed treatment regimens. Factors such as peer pressure, desire for independence, and rebellion against perceived restrictions can impact their adherence to blood sugar monitoring, insulin administration, and dietary recommendations.
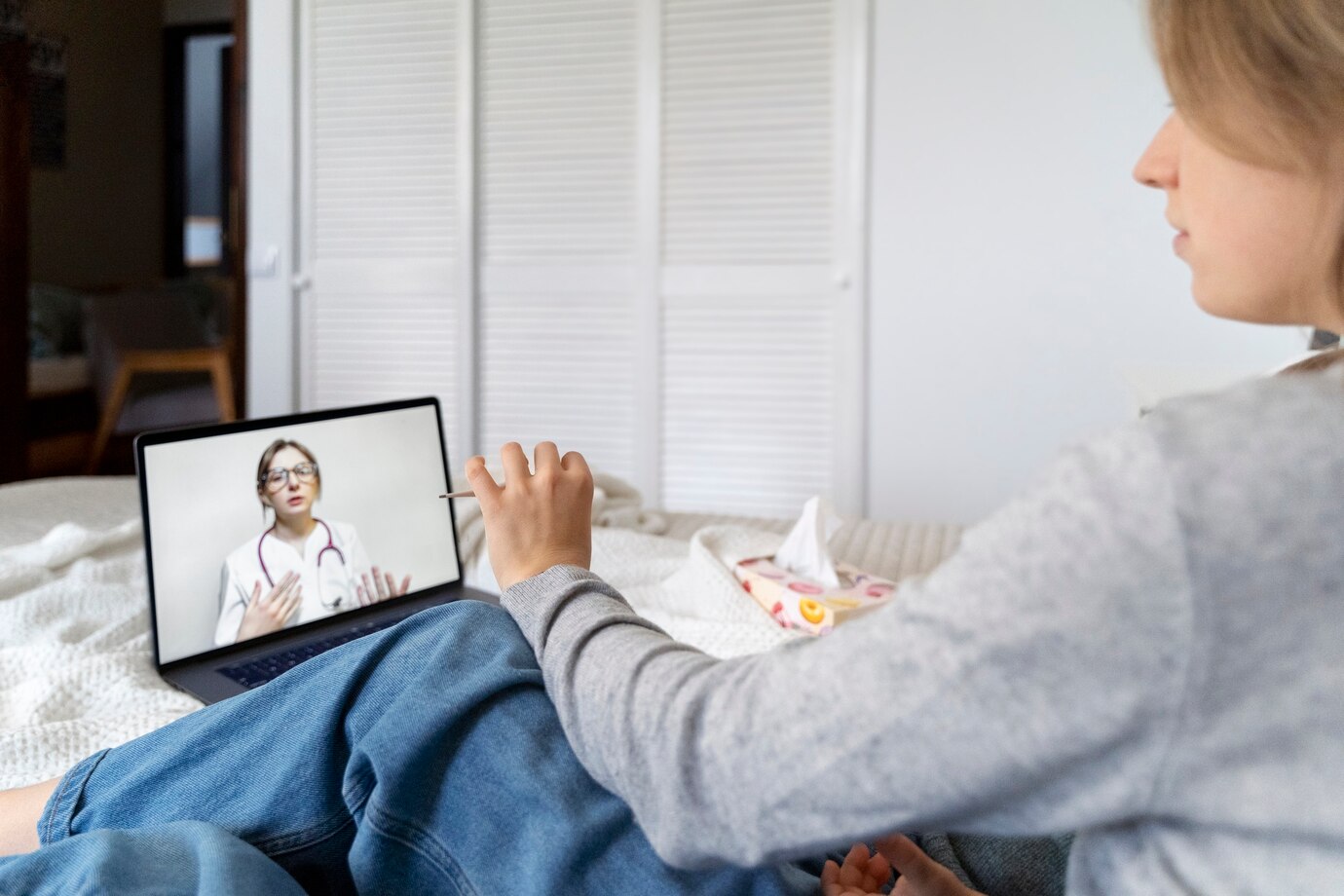
Healthcare providers and caregivers play a crucial role in supporting adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes in overcoming these challenges. Open and non-judgmental communication is key to understanding their concerns and addressing any barriers they may face. Encouraging regular communication between adolescents, their families, and healthcare providers can help identify and address any issues related to treatment adherence.
In addition to communication, it is important to create a supportive environment that fosters self-management skills and encourages autonomy. Providing resources such as diabetes management apps, support groups, and educational materials can empower adolescents to actively participate in their own care. By involving them in decision-making and goal-setting, they can develop a sense of ownership and responsibility for their health.
It is worth noting that the challenges associated with Type 1 Diabetes extend beyond physical health. According to NCBI, adolescents with chronic diseases, including Type 1 Diabetes, may experience lower life satisfaction, mental health problems, and reduced peer support compared to their healthy peers. Therefore, addressing their emotional well-being alongside their physical health is crucial for comprehensive support.
By providing tailored support and addressing the specific needs of adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes, we can empower them to effectively manage their condition, improve their quality of life, and promote their overall well-being.
Social and Emotional Well-being
When supporting teens with chronic illness and mental health issues, it is essential to address their social and emotional well-being. Adolescence is a time of significant social and emotional development, and chronic illness can pose unique challenges in this regard. Two key aspects to consider are peer relationships and self-esteem, as well as coping with stress and anxiety.
Peer Relationships and Self-esteem
Teens with chronic illness often face concerns about their physical appearance, independence, and relationships with peers, which can complicate their development during adolescence [2]. This can lead to self-esteem issues and concerns about acceptance.
To support teens in maintaining positive peer relationships and fostering self-esteem, it is important to encourage them to spend time with friends and engage in activities they enjoy. Open communication about their illness and concerns can help friends understand and be supportive. Having honest discussions with the teen about what they feel comfortable sharing with peers can help them navigate social situations more confidently.
Coping with Stress and Anxiety
Living with a chronic illness can be stressful and may lead to increased anxiety in teens. It is crucial to provide them with effective coping strategies to manage these emotions. Teaching problem-solving skills, stress management techniques, and relaxation exercises can empower teens to effectively cope with stress and anxiety.
Encouraging open communication with healthcare professionals is vital so that teens feel comfortable discussing their concerns and seeking appropriate support and guidance. Additionally, if necessary, involving mental health professionals can provide additional tools and resources for managing stress and anxiety related to their chronic illness.
By addressing the social and emotional well-being of teens with chronic illness, we can help them navigate the challenges they face more effectively. Supporting their peer relationships, fostering self-esteem, and equipping them with coping mechanisms will contribute to their overall well-being and resilience in managing their conditions.
Overcoming Barriers
Supporting teens with chronic illness and mental health issues requires addressing various barriers that can hinder their well-being and access to appropriate care. Two significant barriers to overcome are racial and ethnic disparities and the need for effective mental health support.
Racial and Ethnic Disparities
Adolescents from communities of color often face higher rates of chronic medical conditions and experience poorer health outcomes. Implicit biases among healthcare professionals, social determinants of health, and inadequate access to medical care contribute to these disparities. It is crucial to recognize and address these disparities to ensure equitable support for all teens, regardless of their racial or ethnic background.
To address racial and ethnic disparities, healthcare professionals need to undergo cultural competency training and increase awareness of their own implicit biases. By understanding the unique challenges faced by adolescents from communities of color, healthcare providers can provide more tailored care and support. Additionally, efforts should be made to improve access to medical care and resources for underserved communities, ensuring that all teens have equal opportunities for optimal health and well-being.
Effective Mental Health Support
Adolescents with chronic medical conditions often experience psychiatric comorbidity and are at an increased risk for mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety, and behavioral disorders [5]. Effective mental health support is crucial in helping these teens navigate the challenges they face.
Schools play a vital role in providing mental health support to students. School counselors and mental health professionals can offer individual counseling, group therapy, and psychoeducation programs tailored to the unique needs of adolescents with chronic illnesses. Creating a safe and supportive environment within schools can help reduce the stigma surrounding mental health issues and encourage teens to seek help when needed.
Collaboration between healthcare providers, school personnel, and families is essential in ensuring comprehensive and coordinated care for teens with chronic illness and mental health concerns. Open lines of communication and shared decision-making can help create a holistic support system that addresses both medical and mental health needs.
The global crises we face, such as the COVID-19 pandemic and geopolitical conflicts, have further exacerbated mental health issues among students [4]. It is important for schools and healthcare providers to be vigilant in identifying and addressing mental health challenges, providing appropriate interventions, and connecting teens with the necessary resources.
By addressing racial and ethnic disparities and providing effective mental health support, we can empower teens with chronic illness to better navigate their journey and support their overall well-being. Through a collaborative and inclusive approach, we can create a more equitable and supportive environment for all adolescents, irrespective of their health conditions or backgrounds.
References
- [1]: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC555640/
- [2]: https://www.stanfordchildrens.org/en/topic/default?id=psychological-complications-of-chronic-illness-in-teens-90-P01658
- [4]: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10217808/
- [5]: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9034877/
Similar articles



















.jpeg)









.jpg)




























.jpg)
















.avif)





















